A company's security team detected unusual network activity linked to a potential malware infection. As a forensic analyst, your mission is to investigate a memory dump, identify the malicious process, extract artifacts, and uncover Command and Control (C2) communications. Using Volatility3, analyze the attack, trace its origin, and provide actionable intelligence.
Category: Endpoint Forensics
Tools: Volatility 3
Q1: Our first step is identifying the initial point of contact the malware made with an external server. Can you specify the first IP address the malware attempted to communicate with?

We have memory dump that was already infected my "Qbot" malware and we also have the output of windows.filescan and windows.netscan in a text file as well which we only have Volatility 3 to solve this lab.
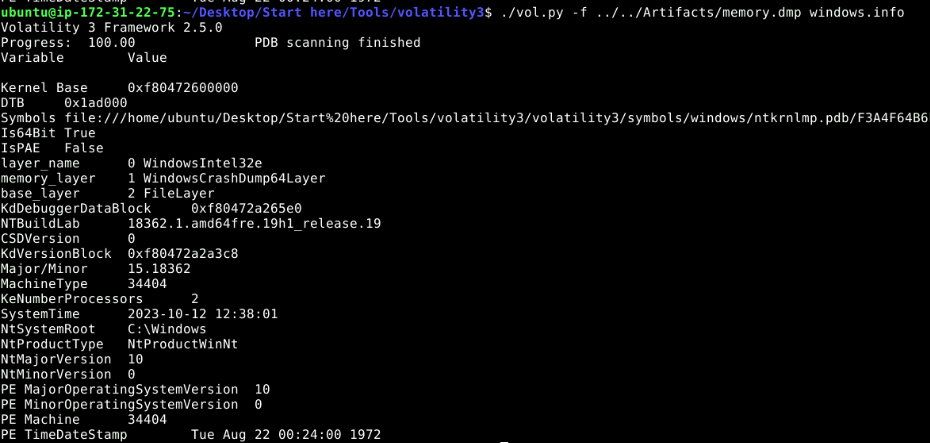
Since we have result of both plugin, it is obvious that this memory dump belongs to Windows host.
Command : ./vol.py -f ../../Artifacts/memory.dmp windows.info

I displayed process tree first to find any suspicious child process under explorer.exe which indicates the execution of malware by user which I noticed that EXCEL.EXE which has the process number (PID) of 4516, knowing the background of QBot malware that often sent as Microsoft Excel attachment in the email and trick user to execute it and it will target banking credential, browser session of the victim (Qbot known as banking trojan so its financially motive malware), then this process is definitely stand out from the rest.
Command : ./vol.py -f ../../Artifacts/memory.dmp windows.pstree

I tried to display the command line to see which file was opened with this process but seem like I need another approach here.
Command : ./vol.py -f ../../Artifacts/memory.dmp windows.cmdline --pid 4516

There is a plugin in Volatility 3 that will dump all files associated with specify process so I used it and then discovered that this process was opened Payment.xls.
Command : ./vol.py -f ../../Artifacts/memory.dmp windows.dumpfiles --pid 4516

Now we can calculate SHA256 hash of this file to answer Q5 and search it on VirusTotal.

VirusTotal picked it up rightaway which telling us how the macro embbeded inside this file work (if we logged in) and we can now confirm that this is definitely Qakbot malware.
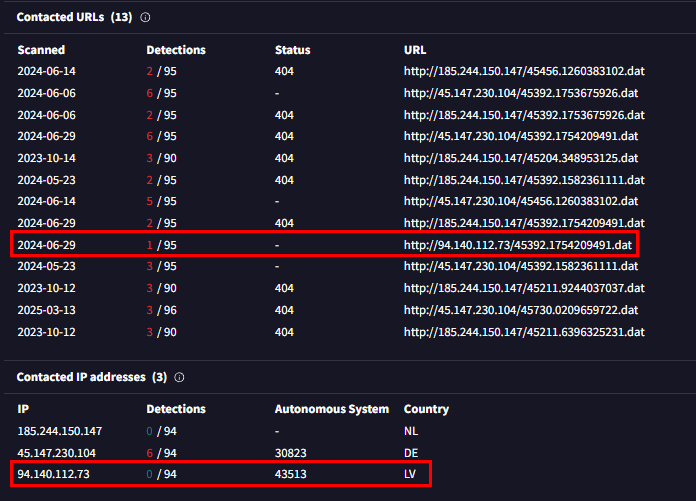
Next to find out about the IP address to answer this question, we have to take a look at the Contacted URLs and Contacted IP addresses right here and we can see that there is only 1 IP address that match the format of this question.

We can confirm that the malware really reached this IP address from the result of windows.netscan plugin but it does not display the process name or PID here.
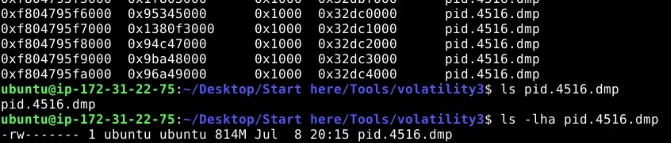
Lets dig it a little bit deeper by dumping the memory of this process.
Command : ./vol.py -f ../../Artifacts/memory.dmp windows.memmap --pid 4516 --dump
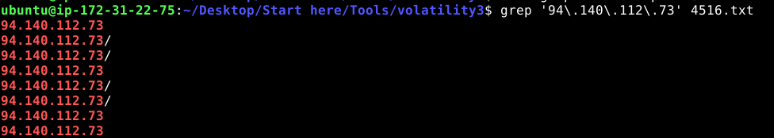
Now we can see that this process was really attempted to reach this IP address.
Command : strings pid.4516.dmp > 4516.txt and grep '94\.140\.112\.73' 4516.txt
94.140.112.73
Q2: We need to determine if the malware attempted to communicate with another IP. Which IP address did the malware attempt to communicate with again?
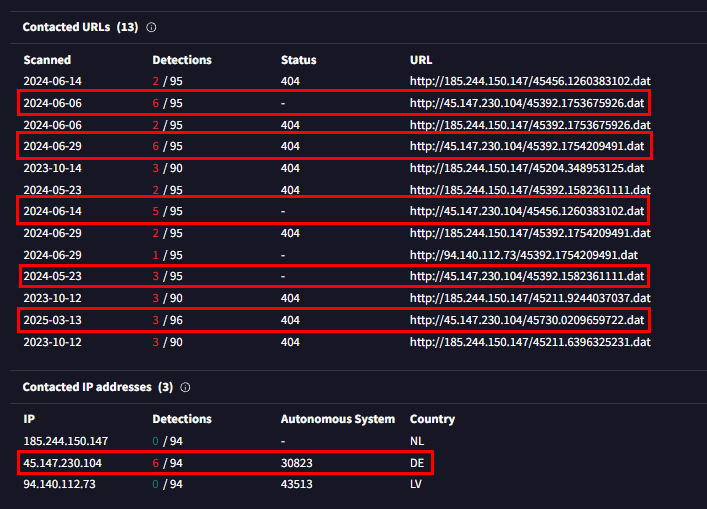
Going back to VirusTotal then we can see that there is one IP address that matchs the answer format of this question.

windows.netscan result also picked it up as well.

Then we can see that it really fetched the .dat file from this IP address with HTTP GET request and now we have the answer of all the questions of this lab.
Command : grep '45\.147\.230\.104' 4516.txt -B 5 -A 1
45.147.230.104
Q3: Identifying the process responsible for this suspicious behavior helps reconstruct the sequence of events leading to the execution of the malware and its source. What is the name of the process that initiated the malware?
EXCEL.EXE
Q4: The malware's file name is crucial for further forensic analysis and extracting the malware. Can you provide its file name?
Payment.xls
Q5: Hashes are like digital fingerprints for files. Once the hash is known, it can be used to scan other systems within the network to identify if the same malicious file exists elsewhere. What is the SHA256 hash of the malware?
3cef2e4a0138eeebb94be0bffefcb55074157e6f7d774c1bbf8ab9d43fdbf6a4
Q6: To trace the origin of the malware and understand its development timeline, can you provide the UTC creation time of the malware file?
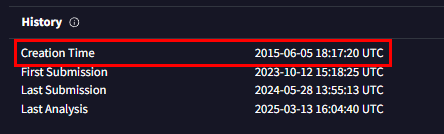
Look up the History section under "Details" tab then we have the creation timestamp of this excel Qbot malware which is the answer of this question.
2015-06-05 18:17
https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf-challenges/achievements/Chicken_0248/qbot/